- Home
- 資料
- 1996Academy of Sciences of Belarus THE CHERNOBYL CATASTROPHE CONSEQUENCES IN THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS National Report
チェルノブイリ事故10周年ベラルーシ科学アカデミー報告書
1996Academy of Sciences of Belarus THE CHERNOBYL CATASTROPHE CONSEQUENCES IN THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS National Report



(無断転載はお断りしますm(_ _)m info@kakehashi.or.jp まで)
〇目次
〇

INTRODUCTION}
April 26, 1986 – a tragic day that brought the most severe ordeals to the long-suffering Belarussian land. For ten years already the Republic of Belarus has lived under the conditions of environmental radioactive contamination caused by the accident at the Chernobyl NPP nuclear reactor.
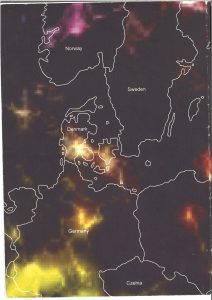
The Chernobyl tragedy is the largest radiational catastrophe that has ever occurred on this planet. The radioactive blow-outs after the Chernobyl NPP catastrophe reached many states. The largest amount of them (according to experts’ estimations 70 %) fell out on the Belarus territory.
It is not for the first time that great ordeals have fallen to the lot of the Belarussian people. During the Great Patriotic War every fourth citizen of Belarus perished, but not everybody knows that the Chernobyl tragedy affected all citizens as well. First of all, it relates to the initial period of the accident when the radionuclides, including short-lived, spread on all the territory. 1840951 people including 483869 children and adolescents under 17 years old, inhabit 3221 villages and towns on the radioactively contaminated territories. The radiation dose on some of them reaches 5 mSv per year and higher. There has been a steady increase of the morbidity rate and socio-psychological tension. Particular concern has arisen over the increase of thyroid gland pathologies, including thyroid gland cancer among children.
The damage caused to the republic by the Chernobyl catastrophe, the catastrophe scales demanded the adoption of emergency measures by the Government of Belarus. Being aware of the global character of the catastrophe and of threatening consequences for republic health, the Supreme Soviet announced the whole territory of the republic to be a zone of ecological calamity. At the initial stage of the post-accident period 24.7 thousand people were evacuated. Up to now 131.2 thousand people from the contaminated areas have been resettled. For the resettlement of such a number of people and for the organization of life-support systems in the radioactively contaminated regions new settlements and working places, enterprises and organizations re-specialization, a network of schools, children’s pre-school institutions, health care establishments, gas pipelines, new electric lines, etc. are needed. This work is still far from completion and requires large investments.
10 years have passed since the Chernobyl NPP accident but some of the problems born by the catastrophe have not been solved, in spite of all the measures undertaken, but in some realms they have become even worse. This is bound up, first of all, with a high collective dosage absorbed by the population, with difficulties in forecasting and prophylactics of remote radiational effects, with ecological and economic crisis. The consequences of the disaster greatly affect all the aspects of vital activities of the affected regions and the state as a whole. That is why the planning and realization of measures to overcome the catastrophe consequences should not be reduced to only radiation protection measures.
This is the position we adhere to and will continue to do so, while elaborating measures of intervention and protection.
The State Programme for overcoming the catastrophe consequences has been elaborated and is being implemented in the Republic of Belarus. The Supreme Soviet has adopted the laws “On Social Protection of Citizens Affected by the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Catastrophe” and “On legal treatment of Territories Affected by Radioactive Contamination As a Result of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Catastrophe”. These laws and other legislative acts determine the State policy that aims to protect the victims health, to provide the population in contaminated territories with safe living conditions, to overcome and diminish the negative socio-psychological, economic and ecological catastrophe consequences.
Significant and in many respects unique material has been accumulated over the years since the Chernobyl NPP catastrophe. This includes the results of radiation effect on people, flora and fauna, abiotic components of the natural environment. The experience of organizing and implementing measures to reduce its negative effects has also been gained.
Time obliterates the most acute moments in memory. To some of those who did not personally face the disaster it may seem that the Chernobyl problem has lost its topicality. The biggest catastrophe of the century is increasingly forgotten and some people consider it as something belonging to the past. But it is not so for the Belarussian people.
Scientists, state leaders, international organizations concerned understand clearly that the unique situation as a result of the Chernobyl NPP accident must be used completely for improving the knowledge about the possible consequences of the similar catastrophes, for investigation and accumulation of experience of practical realization of protection measures complex under the conditions of large-scale radioactive contamination of the territory. It creates good prerequisites for effective and mutually beneficial international co-operation on overcoming of the catastrophe consequences.
We hope that this report which sums up the results of 10-years research and overcoming the accident’s consequences in Belarus, will contribute to a better understanding of the situation in our Republic, will be helpful for further works on overcoming the Chernobyl catastrophe consequences and for determining priorities for rendering international aid, so necessary, to the Belarussian people.
I.A.Kenik L.M.Sushchenya
CHAPTER 1
RADIOECOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF THE CHERNOBYL NPP CATASTROPHE
CHAPTER 2
ECONOMIC DAMAGE AND STATE POLICY ON THE OVERCOMING OF THE CHERNOBYL NPP CATASTROPHE CONSEQUENCES
chapter3
MEDICAL AND SOCIO-PSYCHOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF THE CHERNOBYL CATASTROPHE
AGRO-INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTION UNDER THE CONDITIONS OF RADIOACTIVE CONTAMINATION}
DECONTAMINATION THE MAINTENANCE OF ALIENATION AND SETTLING OUT ZONES
SCIENTIFIC PROVISION OF THE PROBLEMS OF OVERCOMING THE CHERNOBYL CATASTROPHE CONSEQUENCES
INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION
CONCLUSION}
The estimation of radioecological, medico-biological, economic and social consequences of the Chernobyl catastrophe has shown that unimaginable damage was incurred on Belarus and its territory became the zone of ecological calamity. Summarizing the data represented in the National report, it should be concluded that:
{¥} The Chernobyl NPP catastrophe has led to the radioactive contamination of almost a fourth part of the territory of Belarus where there lived 2.2 million people. For the past period 131.2 thousand of people have been resettled. 68 thousand of flats and individual houses, schools – for 29.5 thousand of places, pre-school children’s establishments – for 12.2 thousand of places, hospitals – for 1.8 thousand of patients etc. have been built. The damage caused to the republic by the Chernobyl catastrophe makes up 32 annual budgets of the republic of the pre-accident period in account for the 30-years period for its overcoming.
{¥} Radioecological situation in Belarus is characterized by complexity and heterogeneous contamination of the territory by different radionuclides and their presence on all the components of the environment. It stipulates the plurality of ways of external and internal irradiation of the population and jeopardizes its health.
{¥} There is registered the worsening of the population’s state of health, of evacuated and inhabiting the contaminated areas as well, with 2-10 and more times increase of the number of somatic diseases, including oncological diseases, there are disorders in the metabolic processes and functions of main systems of the organism (immune, endocrine, cardiovascular and others). The demographic indices (the birth rate is decreasing and mortality is increasing) are decreasing. Particular concern causes the children’s morbidity growth and genetic consequences of the accident (increase of congenital defects).
{¥} The contamination of agricultural lands has stipulated in the neighboring the Chernobyl NPP zone the impossibility of their use for food production. On the other lands it has been required to re-profile the farms and create new technologies of the agricultural production that leads to additional expenditures.
{¥} There have been revealed the destructive tendencies in all spheres of the life activity of people who experienced radiation effects. The processes of social adaptation and socio-psychological support of the population inhabiting the radionuclides contaminated territory and resettled as well, require considerable optimization.
In spite of that for ten years passed after the Chernobyl catastrophe, the discrepancy of its estimation has not been overcome completely. Moreover, there is a tendency for understatement of the catastrophe consequences, bringing it down to the ordinary NPP incident. At the same time, the radioecological, medico-biological, socio-psychological, economic and other Chernobyl consequences considered in this report show that the problems born by the Chernobyl catastrophe on April 26, 1986 will remain actual for long.
The minimization and overcoming of the consequences of radiation catastrophe of such a scale is the most complicated task requiring huge material and financial resources.
Taking into account the radioactive post-accident contamination of many countries of Europe, Asia and America it should be admitted that the consequences of the nuclear catastrophe may have global character. While there exist atomic stations, nuclear weapons and radioactive materials (their production, use and processing), there remains the danger of nuclear incidents. The experience of the liquidation of the Chernobyl catastrophe consequences has shown that the achievements of world science and practices are insufficient and recommended measures are often of small effectiveness. This requires the consolidation of efforts of all man-kind for the elaboration of effective measures of protection from nuclear accidents and the overcoming of the Chernobyl catastrophe consequences.